Introduction
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) has become increasingly popular in modern vehicles, especially in mid-sized cars and fuel-efficient models. This article aims to provide a detailed evaluation of CVT based on user experiences and expert advice from the VOZ forum. We’ll delve into its history, workings, benefits, drawbacks, and real-world feedback to help you decide if a CVT is right for your driving needs.
History and Concept of CVT
Overview of CVT
The CVT, or Continuously Variable Transmission, is a type of automatic transmission that can change seamlessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratios. Unlike traditional transmissions that have a fixed number of gears, CVT adjusts the gear ratio continuously, providing a smooth driving experience.
Historical Development
- Early Concepts: The concept of CVT dates back to the 15th century, proposed by Leonardo da Vinci. He conceptualized a belt and pulley system that could change speeds continuously.
- Early 20th Century: The first practical application of CVT was in the Van Doorne’s CVT, developed in the 1920s by Dutch inventors Hub van Doorne and his brother Willem.
- Modern CVT: Became more prevalent in the automotive industry in the late 20th century, particularly in Japanese cars. Subaru was among the pioneers, using CVTs in their Justy model in the late 1980s.
Technological Advancements
Over the years, CVT technology has evolved significantly, incorporating advanced materials and electronic controls to improve durability and performance. Modern CVTs are more reliable and efficient than their predecessors.
- Late 1990s: Introduction of metal belts and advanced hydraulic systems.
- 2000s: Adoption of electronic controls for smoother and more responsive operation.
- 2010s: Integration of hybrid systems and further optimization for fuel efficiency.
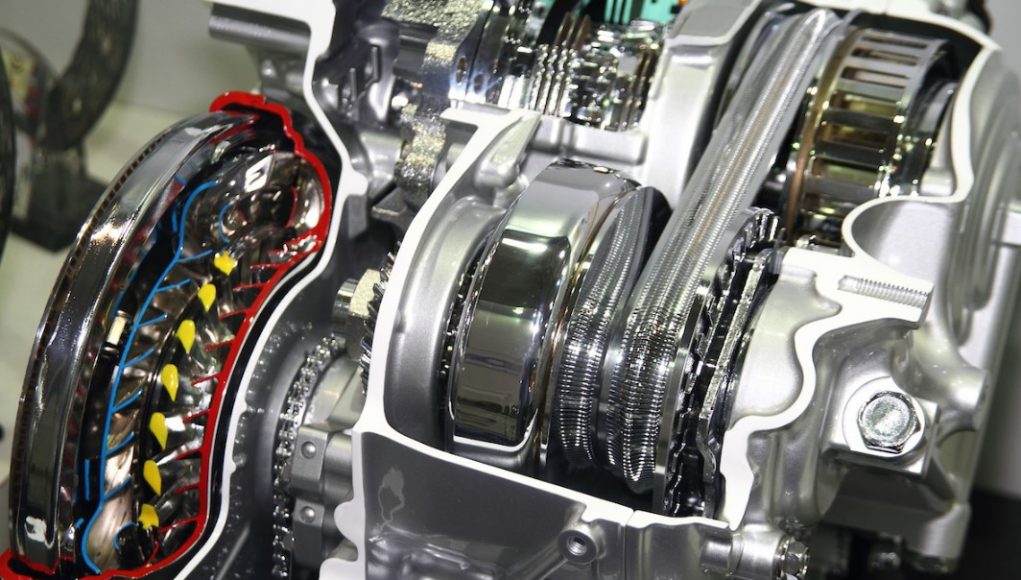
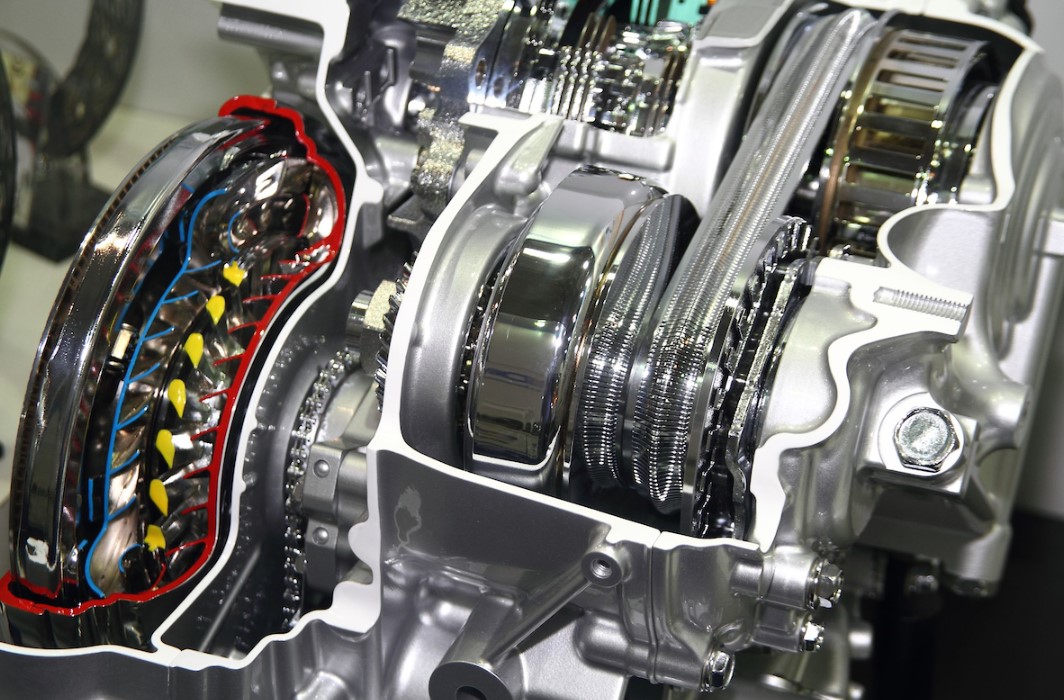
How CVT Works
Basic Structure
- Pulley System: The CVT uses a belt and two pulleys – a drive pulley (connected to the engine) and a driven pulley (connected to the wheels).
- Control System: It adjusts the diameter of the pulleys to change the gear ratio seamlessly.
- Reversing Mechanism: A specific arrangement to change the direction of movement.
Operation Principle
- Variable Gear Ratio: Unlike traditional transmissions, CVT doesn’t have fixed gears. The ratio changes continuously, allowing the engine to operate in its optimal power range, enhancing fuel efficiency.
Real-World Examples
- Starting: When starting from a stop, the CVT adjusts to a lower ratio to provide more torque.
- Acceleration: As you accelerate, the CVT smoothly transitions to a higher ratio for efficient power delivery.
- Cruising: During steady cruising, the CVT maintains an optimal ratio for fuel efficiency.
Advantages of CVT
Fuel Efficiency
CVTs are known for their superior fuel efficiency compared to traditional automatic transmissions (AT). The CVT can keep the engine operating at its most efficient RPM, reducing fuel consumption.
- Example: The Honda Accord 2024 with CVT offers better fuel economy compared to its AT variant.
Smooth Driving Experience
CVTs provide a seamless and smooth driving experience without the noticeable shifts found in traditional gearboxes.
- Example: Users praise the smoothness of the Toyota Camry equipped with a CVT.
Lower Production and Maintenance Costs
The simpler design of CVTs, with fewer moving parts, generally results in lower manufacturing costs and simpler maintenance routines.
- Comparison: Routine maintenance costs for CVTs are typically lower than for ATs.
Disadvantages of CVT
Throttle Response and Driving Feel
CVTs often have a delayed throttle response, which can affect acceleration and overall driving dynamics.
- User Feedback: Many Nissan X-Trail owners report a sluggish response when accelerating.
Durability and Repair Costs
While CVTs can be cheaper to maintain routinely, they tend to be more expensive to repair when problems arise due to their complex design.
- User Experience: Nissan owners with Jatco CVTs often face high repair costs for belt replacements.
Suitability for High Torque Vehicles
CVTs are less suitable for high-torque applications, such as in heavy SUVs or performance cars, due to their limited ability to handle high stress.
- Example: Sports cars rarely use CVTs because they cannot handle the high torque requirements.
Comparison with Automatic Transmissions (AT)
Driving Experience
- CVT: Offers a smooth, gearless experience ideal for city driving.
- AT: Provides a more engaging and responsive driving experience, better suited for spirited driving and diverse terrains.
Cost and Durability
- CVT: Lower routine maintenance costs but higher repair costs and potentially shorter lifespan.
- AT: Higher maintenance and repair costs, but generally more durable.
Comparison Table: CVT vs. AT
| Feature | CVT | AT |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher | Moderate |
| Smoothness | Very smooth | Noticeable gear shifts |
| Throttle Response | Delayed | Immediate |
| Maintenance Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Repair Cost | Higher | Moderate |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
Real-World User Experience from VOZ
Advantages Highlighted
- Smoothness and Efficiency: Many users appreciate the smooth driving experience and fuel efficiency.
- Long-Term Reliability: Some users report no issues even after several years of usage.
Common Complaints
- Throttle Lag: Noticeable delay when accelerating.
- Repair Issues: Difficulties in finding affordable and reliable repair services, especially for belt replacements.
Brand-Specific CVT Quality
Toyota
- Durability: Generally regarded as the most reliable, with smooth performance.
Nissan
- Issues: Frequent complaints about durability and performance, particularly with Jatco CVTs.
Honda
- Mixed Reviews: Generally positive, but some concerns about long-term durability.
Feedback from Different User Groups
Korean Car Enthusiasts
- Skepticism: Concerns about the complexity and repair costs of CVTs.
Japanese Car Owners
- Preference: Favor Toyota’s CVTs, cautious about Nissan’s and Honda’s versions.
X-Trail Users
- Smooth Ride: Positive feedback on smoothness but note sluggish acceleration.
General Feedback
- City Driving: Most users are satisfied with CVTs in urban settings.
- Highway Driving: Preference for traditional ATs for a more engaging experience.
Tips and Best Practices for Using CVT
Using Sport Mode
- Sport Mode: Switch to S mode for better throttle response and higher RPMs when needed.
Maintenance and Care
- Oil Use: Use the correct type of transmission fluid and avoid overfilling or underfilling.
- Regular Check-ups: Regularly check and replace transmission fluid at reputable service centers.
Conclusion and Advice
CVT transmissions offer a smooth and efficient driving experience, particularly suited for city driving. However, they come with some drawbacks such as throttle response and potential repair costs. For those who prioritize a smooth, fuel-efficient ride, CVTs are a good choice. However, if you prefer a more dynamic driving experience and robust performance, an automatic transmission might be more suitable.
Key Takeaway
CVT transmissions have their unique benefits and drawbacks. It’s essential to consider your driving needs and preferences when choosing between a CVT and other transmission types. Regular maintenance and understanding the limitations of CVTs can enhance their longevity and performance.
FAQs
1. What is the primary benefit of a CVT transmission?
- The primary benefit of a CVT transmission is its smooth, gearless driving experience and superior fuel efficiency.
2. Are CVTs reliable in the long term?
- CVTs can be reliable if properly maintained, but they may have higher repair costs and durability concerns compared to traditional automatic transmissions.
3. How does a CVT transmission compare to an automatic transmission in terms of driving feel?
- CVTs offer a smoother, more seamless driving experience, while automatic transmissions provide a more engaging and responsive feel.
4. What should I consider when maintaining a CVT transmission?
- Use the correct transmission fluid, avoid overfilling or underfilling, and have regular check-ups at reputable service centers.
5. Is a CVT suitable for all types of vehicles?
- CVTs are best suited for city driving and vehicles with moderate torque requirements. They are less ideal for high-torque vehicles like heavy SUVs and 4x4s.